Over the next three years, a firm is expected to earn economic profit of $200,000 in the first year, $300,000 in the second year, and $250,000 in the third year. After the end of the third year, the firm goes out of business. If the risk-adjusted discount rate is 9 percent for each of the next three years,
1. The firm can be sold today for a price of $______________.
2. The value of the firm is $______________.
The value of the firm is the sum total of the present value of economic profits of each of the three years at the given risk-adjusted discount rate.
Calculate the value of the firm -
Value = [$200,000/(1+0.09)1] + [$300,000/(1+0.09)2] + [$250,000/(1+0.09)3]
Value = [$200,000/(1.09)1] + [$300,000/(1.09)2] + [$250,000/(1.09)3]
Value = [$200,000/1.09] + [$300,000/2.18] + [$250,000/3.27]
Value = $183486.24 + $137614.68 + $76,452.60
Value = $397,553.52
Thus,
The firm can be sold today for a price of $397,553.52.
The value of the firm is $397,553.52.
You might also like to view...
The relationship between the price level and net exports is:
A. perfectly correlated. B. negative. C. uncorrelated. D. positive.
Exhibit 4-3 Supply and demand curves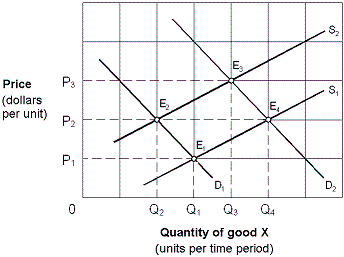
A. E1. B. E2. C. E3. D. E4.
Which of the following indicates taking an action to reverse the effect of official intervention on the domestic money supply?
A. Playing by the "rules of the game" B. Implementing capital controls C. Sterilization D. Adjusting the country's interest rates
Refer to the payoff matrix. Suppose that Speedy Bike and Power Bike are the only two bicycle manufacturing firms serving the market. Both can choose large or small advertising budgets. If this is a repeated game with no cooperation or reciprocity, cell A:
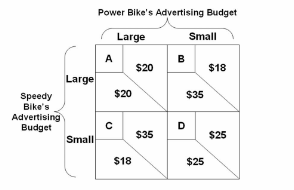
A. is not the expected outcome of this game.
B. is the expected outcome of this game, and it is both a Nash equilibrium and a prisoner's dilemma.
C. is the expected outcome of this game, but it is neither a Nash equilibrium nor a prisoner's
dilemma.
D. is the expected outcome of this game, and it is a Nash equilibrium but not a prisoner's
dilemma.