A 0.025-kg block on a horizontal frictionless surface is attached to an ideal massless spring whose spring constant is 150 N/m. The block is pulled from its equilibrium position at x = 0.00 m to a displacement x = +0.080 m and is released from rest
The block then executes simple harmonic motion along the horizontal x-axis. When the displacement is x = 0.024 m, what is the kinetic energy of the block? A) 0.44 J
B) 0.41 J
C) 0.46 J
D) 0.49 J
E) 0.52 J
A
You might also like to view...
Coulomb's Law: Two equal and opposite charges are a small distance apart, forming an electric dipole. A positive charge +q is placed above these charges, as shown in the figure, equidistant from both of them. Which diagram below best gives the direction of the net force the dipole exerts on the charge +q?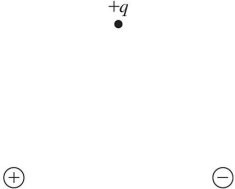
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
C. 
D. 
A ten loop coil of area 0.23 m2 is in a 0.047 T uniform magnetic field oriented so that the maximum flux goes through the coil. The coil is then rotated so that the flux through it goes to zero in 0.34 s
The average emf induced in the coil during the 0.34 s is A) 3.2 × 10-3 V. B) 0. C) 3.2 × 10-2 V. D) 3.2 × 10-1 V. E) 1.0 V.
Light travels for about ________ to reach the Sun's surface from the Sun's core, and about ________ to reach Earth from the Sun's surface.
A. 1 minute; 8 seconds B. 100 years; 8 minutes C. 100 years; 8 seconds D. 16 million years; 8 minutes
Two blocks with masses 2.0 kg and 3.0 kg are placed on a horizontal frictionless surface. A light spring is placed in a horizontal position between the blocks. The blocks are pushed together, compressing the spring, and then released from rest. After contact with the spring ends, the 3.0-kg mass has a speed of 2.0 m/s. How much potential energy was stored in the spring when the blocks were
released? a. 15 J b. 3.0 J c. 6.0 J d. 12 J e. 9.0 J