A monopolist will
a. never produce at an output level where marginal cost is positive
b. always produce at an output level where marginal revenue is positive
c. seek network externalities whenever switching costs are high
d. always produce where marginal revenue exceeds price
e. never produce where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost
B
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph, which shows the supply and demand curves for dollars in the pound/dollar market, to answer the next question,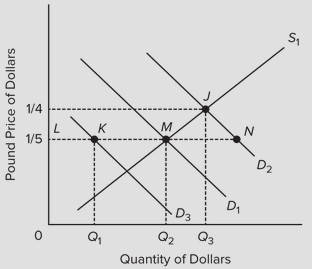 Assume that D1 and S1 are the initial demand for and supply of dollars. Suppose that Britain's demand for dollars increases from D1 to D2. If the British government wishes to fix the exchange rate at the initial level, it should ________.
Assume that D1 and S1 are the initial demand for and supply of dollars. Suppose that Britain's demand for dollars increases from D1 to D2. If the British government wishes to fix the exchange rate at the initial level, it should ________.
A. buy and add more to its dollar reserves B. encourage the British to import more U.S. products C. sell pounds in exchange for U.S. dollars D. sell some of its dollar reserves
Refer to the following graph.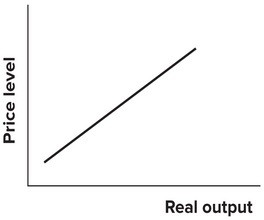 The upward sloping relationship in the diagram represents the:
The upward sloping relationship in the diagram represents the:
A. quantity adjustment curve. B. long-run aggregate supply curve. C. aggregate demand curve. D. short-run aggregate supply curve.
Which of the following is an example of a negative externality?
A. Government funding of public education. B. An increase in government bureaucracy and red tape. C. An increase in the incidence of cancer due to pollution. D. A factory introduces a production process that reduces pollution.
If an American investor buys shares of stock of the German auto manufacturer BMW, the transaction
A. is registered as a debit in the current account, and it decreases private U.S. assets abroad. B. is registered as a credit in the capital account, and it increases foreign private assets in the United States. C. is registered as a debit in the capital account, and it increases private U.S. assets abroad. D. is registered as a credit in the capital account, and it decreases foreign private assets in the United States.