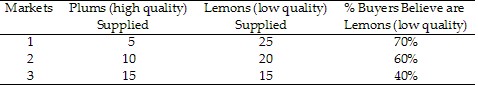
 In Table 9.3, Market 1 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed lemons account for:
In Table 9.3, Market 1 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed lemons account for:
A. about 83.33% of the market.
B. about 71.43% of the market.
C. about 66.67%% of the market.
D. about 42.86% of the market.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The profit maximizing condition for a firm in monopolistic competition is to produce so that
A) marginal cost equals marginal revenue. B) marginal cost equals price. C) average total cost equals price. D) price equals marginal revenue.
The level of saving in Japan has historically been high relative to the level of domestic investment. Based on this information, we would expect that
A) Japan's net exports have been relatively high. B) Japan's capital inflows are positive. C) Japan's private saving is greater than its public saving. D) Japan's net foreign investment has been relatively low.
Assume that the central bank increases the reserve requirement. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the GDP Price Index and the nominal value of the domestic currency in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The GDP Price Index falls, and nominal value of the domestic currency falls. b. The GDP Price Index falls, and nominal value of the domestic currency remains the same. c. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables. d. The GDP Price Index rises, and nominal value of the domestic currency rises. e. The GDP Price Index falls, and nominal value of the domestic currency rises.
According to classical macroeconomic theory, changes in the money supply affect
a. variables measured in terms of money and variables measured in terms of quantities or relative prices b. variables measured in terms of money but not variables measured in terms of quantities or relative prices c. variables measured in terms of quantities or relative prices, but not variables measured in terms of money d. neither variables measured in terms of money nor variables measured in terms of quantities or relative prices