In Table 17.4, 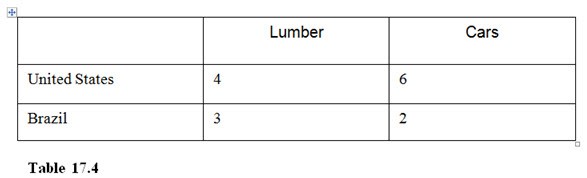
A. Brazil has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in lumber only.
B. the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in cars only.
C. the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in Cars while, Brazil has an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
D. the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The following table provides data for an economy in a certain year. Consumption expenditures1,000Imports600Government purchases of goods and services700Construction of new homes and apartments500Sales of existing homes and apartments600Exports500Government payments to retirees200Household purchases of durable goods300Begining-of-year inventory500End-of-year inventory600Business fixed investment300Given the data in the table, how much did households spend on nondurables and services?
A. 300 B. 700 C. 1,300 D. 1,000
A one-year bond has an interest rate of 0.2% and is expected to rise to 0.5% next year and 1.1% in two years. The term premium for a two-year bond is 0.1% and for a three-year bond is 0.25%
What are the interest rates on a two-year bond and three-year bond according to the liquidity premium theory?
Which of the following is most central to the understanding of the economic crisis of 2008?
a. the decline of the stock market in late 2007 b. the housing boom (2001-2005) and bust (2007-2008) c. the sharp rise in oil prices in 2008 d. unethical investment practices beginning in 2000
If the budget deficit increases then
a. saving and the interest rate rise. b. saving rises and the interest rate falls. c. saving falls and the interest rate rises. d. saving and the interest rate fall.