In making a production decision, an entrepreneur
A. Decides what level of output will maximize profits.
B. Determines plants and equipment.
C. Decides whether to enter or exit the market.
D. Can change both fixed and variable inputs.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If the GDP deflator is 142, by how much have prices changed since the base year?
A) Prices have increased by 42%. B) Prices have increased by 142%. C) Prices have increased by 58%. D) Prices have decreased by 4.2%.
The market for soybeans in Canada consists solely of domestic buyers of soybeans and domestic sellers of soybeans if
a. consumer surplus equals producer surplus in the Canadian soybean market. b. total surplus exceeds consumer surplus in the Canadian soybean market. c. Canada permits international trade in soybeans. d. Canada forbids international trade in soybeans.
Refer to the figure below. In the matrix above: 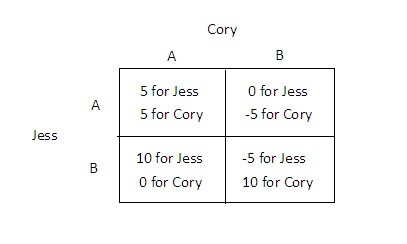
A. both Cory and Jess have the same dominant strategy. B. Jess has a dominant strategy, but Cory does not. C. neither Cory nor Jess has a dominant strategy. D. Cory has a dominant strategy, but Jess does not.
Kris, Taylor and Max are the only three residents in a neighborhood. A public good that would benefit all of them has a one-time installation cost of $900. The value of the public good to each resident is shown in the table below. Any tax plan must be approved by simple majority.ResidentReservation PriceIncomeKris$100$1,000Taylor$200$5,000Max$700$6,000 If the government proposes to pay for the public good with a head tax of $300 per resident, then
A. Max will vote in favor of the tax, but Kris and Taylor will vote against it. B. all three will vote in favor of the tax. C. Max will vote against the tax, but Kris and Taylor will vote in favor of it. D. all three residents will vote against the tax.