In the short run, if a perfectly competitive firm produced at the quantity of productive efficiency, would it generate the highest profit level possible? Why or why not?
In the short run, a firm producing with productive efficiency would not necessarily generate the highest level possible. Productive efficiency occurs at the lowest point on the ATC curve which can be found where MC = ATC. However, this is not likely to be the same as the quantity of profit maximization which is found at the point where MC = MR.
You might also like to view...
Ray buys a new tractor for $118,000 . He receives consumer surplus of $13,000 on his purchase. Ray's willingness to pay is
a. $13,000. b. $105,000. c. $118,000. d. $131,000.
Give an example that shows why price index has to be used to accurately calculate GDP statistics. Avoid using examples given in the text.
What will be an ideal response?
Referring to the Aggregate Demand - Aggregate Supply diagram in Figure 8.1, which box should be filled with the label RGDP* for the macroeconomic equilibrium level of Real Gross Domestic Product? 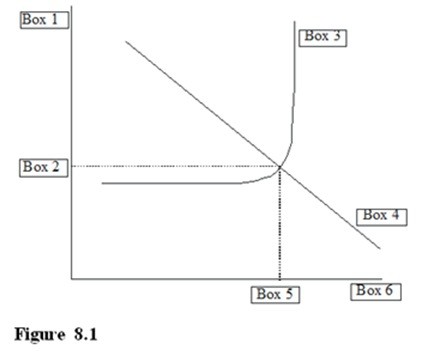
A. Box 1 B. Box 5 C. Box 2 D. Box 6
Suppose the Federal Reserve's short-run response to any change in the economy is to change the money supply to maintain the existing real interest rate. What would happen to money supply if there were a reduction in government purchases? Given the Fed's policy, what would happen in the very short run (before general equilibrium is restored) to output and the real interest rate? What must happen to the LM curve and the price level to restore general equilibrium?
What will be an ideal response?