Find all the second order partial derivatives of the given function.f(x, y) = cos xy2
A. fxx(x, y) = y2 sin xy2; fyy(x, y) = 2[2y2 cos (xy2) - sin (xy2)] ; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = 2y[y2 cos (xy2) - sin (xy2)]
B. fxx(x, y) = -y4 cos xy2; fyy(x, y) = - 2x[2xy2 cos (xy2) + sin (xy2)]; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = - 2y[xy2 cos (xy2) + sin (xy2)];
C. fxx(x, y) = - y2 sin xy2; fyy(x, y) = 2[ sin (xy2)- 2y2 cos (xy2)] ; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = 2y [sin (xy2)-y2 cos (xy2)]
D. fxx(x, y) = - y2 sin xy2; fyy(x, y) = 2y ; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = 2
; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = 2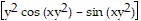
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Solve the problem.Rule: The sum of any two horizontally adjacent numbers is the number immediately below them. Use this rule to complete the array. 
A. 
B. 
C. 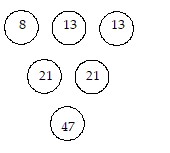
D. 
Expand the quotient by partial fractions.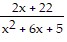
A. 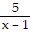 +
+ 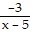
B. 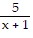 +
+ 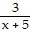
C. 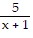 +
+ 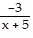
D. 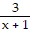 +
+ 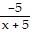
Evaluate the expression for other given values of the variables.(x + 3y)2 for x = 2, and y = 4
A. 14 B. 25 C. 196 D. 28
Find the center, foci, and vertices of the ellipse.36(x - 3)2 + 16(y + 1)2 = 576
A. center at (3, -1)
foci at (3, -1 - 2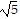 ), (3, -1 + 2
), (3, -1 + 2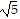 )
)
vertices at (3, 5), (3, -7)
B. center at (-3, -1)
foci at (-3, -1 - 2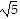 ), (-3, -1 + 2
), (-3, -1 + 2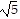 )
)
vertices at (-3, 5), (-3, -7)
C. center at (4, -1)
foci at (4, -1 - 2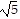 ), (4, -1 + 2
), (4, -1 + 2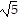 )
)
vertices at (4, 5), (4, -7)
D. center at (-1, 3)
foci at (-1, 3 - 2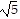 ), (-1, 3 + 2
), (-1, 3 + 2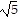 )
)
vertices at (-1, 5), (-1, -7)