Peter studies at the coffee shop around the corner, at the same time that John talks loudly on his cell phone. The costs and benefits of each cell phone call made by John are given by the following table: 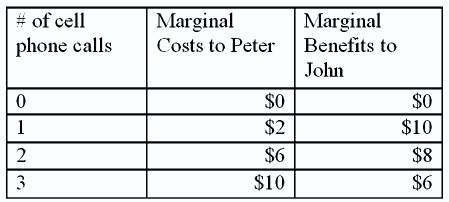 If the both Peter and John could negotiate a settlement without transactions costs, how many phone calls would John end up making if he (John) had the rights to make any calls he liked at the coffee shop?
If the both Peter and John could negotiate a settlement without transactions costs, how many phone calls would John end up making if he (John) had the rights to make any calls he liked at the coffee shop?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
If the government does not provide it, the quantity of a nonexcludable good that private firms will choose to produce is
A. zero. B. more than the optimal amount. C. the optimal amount. D. optimal only if property rights are assigned. E. optimal only if the industry is competitive.
According to the classical model, in the labor market
a. perfect information about the market price by market participants is required. b. the labor market is always in equilibrium. c. prices and wages are perfectly flexible. d. both suppliers and purchasers of labor must know the relevant trading prices. e. All of the above.
Suppose Sarah owns a small company that makes wedding cakes. The accompanying table shows how Sarah's total cost varies depending on the number of wedding cakes she makes each day.Number of Cakes Per DayTotal Cost Per Day0$1001$1802$2203$3004$4005$5206$660 If the market for wedding cakes is perfectly competitive, and wedding cakes sell for $95 each, then Sarah should produce ________ cakes per day.
A. 5 B. 3 C. 6 D. 0
When governments subsidize retraining programs for unemployed workers to learn new skills, they are trying to minimize the effects of which kind of unemployment?
A. Seasonal B. Structural C. Frictional D. Real-wage