If goods X and Y are substitute goods, then an increase in the price of Y, other things being equal,
A) results in a decrease in the amounts of both X and Y consumed.
B) decreases the quantity demanded of Y, but has no effect on the amount of X consumed.
C) results in a decrease in the quantity of Y consumed, but increases the demand for X.
D) has no real effect on the quantity demanded of good Y, but increases the demand for X.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
International capital flows are purchases and sales of ____ across national borders.
A. goods B. financial assets C. services D. commodities
Refer to Figure 12-1. If the firm is charging a price of $12 per unit
A) it is not selling any output. B) it is selling 700 units. C) it is making a profit. D) it breaks even.
The graph shown demonstrates a tax on sellers. Which of the following can be said about the effect of this tax?
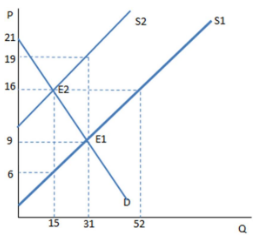
A. The price paid by buyers is greater than that received by sellers, and the difference is the tax wedge.
B. The price paid by buyers is less than that received by sellers, and the difference is the total tax revenue.
C. The price paid by buyers is greater than that received by sellers, and the difference is the total tax revenue.
D. The price paid by buyers and received by sellers is higher than it was before the tax was imposed.
In the long run
A. the expansion path shows how the input marginal products change as the firm's output level changes. B. all inputs are fixed. C. a firm is making the optimal input choice when the marginal rate of technical substitution is equal to the input price ratio. D. both a and b E. none of the above