Monetary policy refers to the government's
A) decisions on how much money to spend.
B) decisions on how much money to collect in taxes.
C) plans for retiring the national debt.
D) management of the money supply and interest rates to achieve macroeconomic objectives.
D
You might also like to view...
The financial crisis of 2008 was triggered by:
A. a speculative bubble in the U.S. housing market. B. austerity measures introduced by the U.S. government to reduce the federal deficit. C. increased trade with China. D. the economic integration of the European Union.
If a particular choice that an individual faces gives him a benefit of $20 but costs $30, the net benefit from making this choice equals:
A) $20. B) $10. C) -$10. D) -$30.
Suppose that the development of a new, improved seed allows all corn farmers in the United States to increase their yields per acre. Since the demand for corn is relatively inelastic, the price of corn in a perfectly competitive market is likely to
a. not change, but farm revenues will fall. b. not change, but farm revenues will rise. c. increase, and farm revenues will fall. d. decrease, and farm revenues will fall.
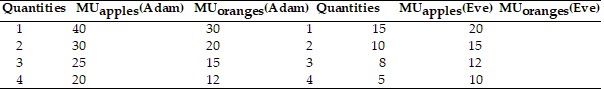 Adam has 3 apples and 3 oranges. Eve has 2 apples and 2 oranges. The marginal utilities for Adam and Eve are summarized in the above table. Adam asks Eve to exchange one of her apples for an orange.
Adam has 3 apples and 3 oranges. Eve has 2 apples and 2 oranges. The marginal utilities for Adam and Eve are summarized in the above table. Adam asks Eve to exchange one of her apples for an orange.
A. Eve will be willing to make the exchange, because her total satisfaction will remain unchanged. B. Eve will be unwilling to make the exchange, because she loses 15 utils of satisfaction. C. Eve will be unwilling to make the exchange, because she loses 5 utils of satisfaction. D. Eve will be willing to make the exchange, because her total satisfaction will increase.