Refer to the information provided in Figure 17.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 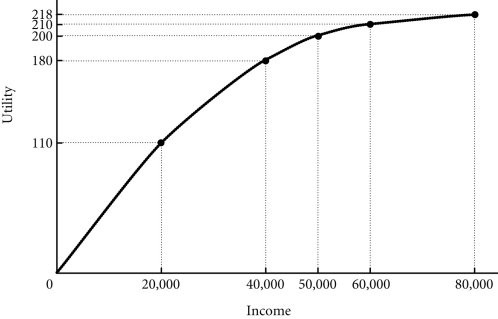 Figure 17.1 Refer to Figure 17.1. John has two job offers when he graduates from college. John views the offers as identical, except for the salary terms. The first offer is at a fixed annual salary of $50,000. The second offer is at a fixed salary of $20,000 plus a possible bonus of $60,000. John believes that he has a 50-50 chance of earning the bonus. What is the expected value of John's income for each job offer?
Figure 17.1 Refer to Figure 17.1. John has two job offers when he graduates from college. John views the offers as identical, except for the salary terms. The first offer is at a fixed annual salary of $50,000. The second offer is at a fixed salary of $20,000 plus a possible bonus of $60,000. John believes that he has a 50-50 chance of earning the bonus. What is the expected value of John's income for each job offer?
A. $25,000 for the first offer and $50,000 for the second offer
B. $50,000 for the first offer and $50,000 for the second offer
C. $50,000 for the first offer and $80,000 for the second offer
D. $50,000 for the first offer and $30,000 for the second offer
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suppose we were analyzing the pound per Swiss franc foreign exchange market. If Switzerland's tax level rises relative to England and nothing else changes, then the:
a. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, causing an uncertain change in the value of the Swiss franc. b. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, causing an appreciation of the Swiss franc. c. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, causing a depreciation of the Swiss franc. d. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, causing an uncertain change in the value of the Swiss franc. e. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, causing an appreciation of the Swiss franc.
If a good has become more scarce, then we know for sure that
a. the demand for it increased. b. the supply of it decreased. c. either the demand for it increased or the supply of it decreased. d. both the supply of it and the demand for it decreased.
A public utility is a classic example of:
A. a natural monopoly. B. perfect competition. C. an oligopoly. D. monopolistic competition.
Price elasticity is defined as the change in quantity demanded relative to a change in
A. the price of substitute products. B. the price of the product. C. the price of complementary products. D. consumer income.