An object is thrown upward at 5.0 m/s, and experiences only the force of gravity once thrown. One second later the object is
A. rising at 5 m/s.
B. neither rising nor falling.
C. falling at 4.8 m/s.
D. rising at 4.8 m/s.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
We observe that a moving charged particle experiences no magnetic force. From this we can definitely conclude that
A) no magnetic field exists in that region of space. B) the particle must be moving parallel to the magnetic field. C) the particle is moving at right angles to the magnetic field. D) either no magnetic field exists or the particle is moving parallel to the field. E) either no magnetic field exists or the particle is moving perpendicular to the field.
What event marks the birth of a star, and what event marks its death?
What will be an ideal response?
The shorter a wave's wavelength, the greater its energy
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
A laboratory apparatus is used to maintain a horizontal slab of ice at -2.2°C so that specimens can be prepared on the surface of the ice and kept close to 0°C. If the ice is 10 cm by 3.8 cm and the laboratory is kept at 16°C, find the cooling rate in watts that the apparatus must provide to the ice.
GIVEN
• A slab of ice in a laboratory
• Ice temperature (Ti) = -2.2°C
• Ice dimensions: 10 cm by 3.8 cm
• Ambient temperature (T?) = 16°C
FIND
• The cooling rate (q) in watts
ASSUMPTIONS
• Air in the laboratory is still
• Effects of sublimation are negligible
• Effects of moisture in the air are negligible
SKETCH
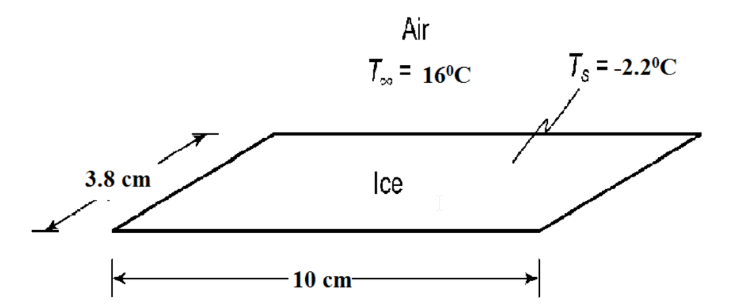
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the mean temperature of 6.9°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.0036 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0242 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 14.51*10-6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71