What are the key differences between how we illustrate a contractionary fiscal policy in the basic aggregate demand and aggregate supply model and in the dynamic aggregate demand and aggregate supply model?
What will be an ideal response?
In the basic aggregate demand and aggregate supply model, contractionary fiscal policy is illustrated by a leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve, with the short-run aggregate supply curve and long-run aggregate supply curve remaining stationary. The dynamic aggregate demand and aggregate supply model takes into account the economy experiencing continuing inflation from year to year and the economy experiencing long-run growth. In the dynamic model, contractionary fiscal policy is illustrated by a rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve which is less than the rightward shifts of the short-run aggregate supply curve and the long-run aggregate supply curve.
You might also like to view...
Michelle Vlasminski, CEO of Michelle Enterprises, has five projects in hand and is considering which, if any, to undertake. Their expected returns are: project A = 12 percent, project B = 7 percent, project C = 10 percent, project D = 9 percent, and project E = 8 percent. If the interest rate is 8.5 percent, which, if any, investment projects will she accept?
a. only project A b. projects A and C c. projects A, C and D d. projects A, C, D and E e. projects A, B, C, D and E
What term is used to denote a tax on imports?
a. gratuity b. ad valorem c. subsidy d. tariff
A change in quantity supplied of a product is the result of a change in:
A. consumer income. B. the state of production technology. C. the cost of producing the product. D. the price of the product.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 3.7 below to answer the following question(s).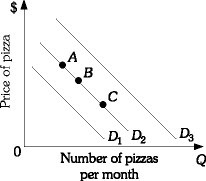 ?Figure 3.7Refer to Figure 3.7. An increase in quantity demanded is represented by the movement
?Figure 3.7Refer to Figure 3.7. An increase in quantity demanded is represented by the movement
A. from D2 to D3. B. along D2 from Point B to point A. C. along D2 from Point B to point C. D. from D2 to D1.