When expectations are rational, disequilibrium in the labor market would exist only temporarily as a result of unpredictable shocks in the economy.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
True
You might also like to view...
An equation that captures how inputs of production are related to output is called a:
A. consumption function. B. GDP deflator. C. production function. D. saving function
To maintain a fixed exchange rate via intervention in the markets, a government should:
a. be ready to crack down on illegal traders. b. be ready to buy the home currency with foreign currency reserves when the home currency's value declines. c. be ready to sell the home currency when the home currency's value declines. d. be ready to borrow funds from international banks when the home currency's value declines.
Suppose that a firm in a competitive market faces the following prices and costs:
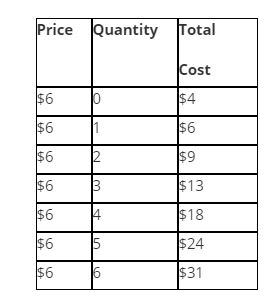
Refer to Table 14-11. The marginal revenue from producing the 5th unit equals
(i) $6.
(ii) the price.
(iii) the marginal cost.
a. (i) only
b. (i) and (ii) only
c. (iii) only
d. (i), (ii) and (iii)
Which type of exchange rate system minimizes external shocks to an economy?
What will be an ideal response?