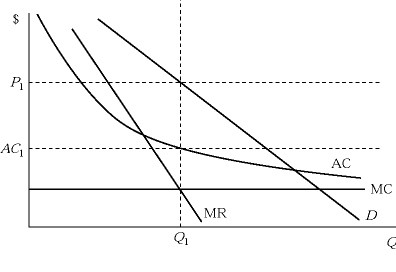
 Figure 11.1If Figure 11.1 depicts the current situation for a monopolistically competitive firm, then in the long run we expect:
Figure 11.1If Figure 11.1 depicts the current situation for a monopolistically competitive firm, then in the long run we expect:
A. the firm to charge a price higher than P1.
B. the firm to produce and sell more than Q1.
C. the average costs of production to decrease below AC1.
D. the firm to charge a price lower than P1.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
If a monopoly is operating on the demand curve where price elasticity is equal to -3, and MR equals 2, then price is equal to
A) 3. B) 2. C) 1. D) 0.
The administrative, enforcement, and compliance costs of collecting taxes in the United States sum to
a. between 1 and 2 percent of the revenues collected. b. between 5 and 6 percent of the revenues collected. c. between 12 and 15 percent of the revenues collected. d. more than half of the revenues collected.
If the quantity of loanable funds demanded exceeds the quantity of loanable funds supplied,
a. there is a surplus so interest rates will rise. b. there is a surplus so interest rates will fall. c. there is a shortage so interest rates will rise. d. there is a shortage so interest rates will fall.
Why would lowering its own interest rates affect a nation's exchange rate?
a. International interest arbitrage (the ability to borrow in low-rate markets and deposit in higher-rate markets) would cause investors to sell domestic currency assets and purchase foreign assets based in other currencies. b. A nation's central bank controls both interest rates and exchange rates. Unfortunately, they do not have sufficient funds to take care of both at the same time. c. When interest rates fall, borrowing is cheaper, spending and GDP rise and so do exports, thus causing the exchange rate to appreciate. d. In the short run, exchange rates have to adhere to PPP; otherwise, traders will make profits by purchasing in the cheap market and selling in the more expensive market, thus aligning exchange rates at the proper level