If a business firm operates indefinitely without covering any of its sunk costs, what happens to the firm's sunk costs?
A) Nothing happens to them; they have ceased to exist.
B) They are distributed across the whole economy.
C) They continue unpaid for as long as the firm fails to make a profit large enough to cover them.
D) They reduce the wealth of the investors who risked their wealth to make mistaken decisions possible.
D
You might also like to view...
In the long run, a firm in monopolistic competition will produce
A) where average total cost is minimized. B) where price equals average total cost but average total cost is not at its minimum. C) zero output. D) any possible amount of output. E) where price equals marginal cost.
Refer to Scenario 12.3. What is the monopoly price of this new drink?
A) 0 B) $3 C) $13.50 D) $16.50 E) $27
Which of the following statements is consistent with a given (i.e., fixed) LM curve?
A) A reduction in the interest rate causes investment spending to increase. B) A reduction in the interest rate causes money demand to decrease. C) A reduction in the interest rate causes an increase in the money supply. D) An increase in output causes an increase in demand for goods. E) An increase in output causes an increase in money demand.
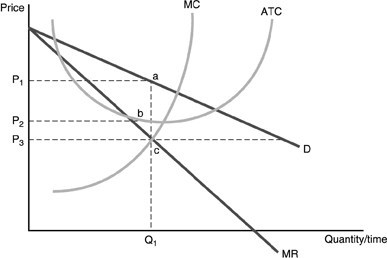 Refer to the above figure. Economic profits for this firm are
Refer to the above figure. Economic profits for this firm are
A. negative and equal to P1bcP2. B. positive and equal to P1abP2. C. negative and equal to P2bcP3. D. positive and equal to P2bcP3.