The figure below illustrates the impact of an export subsidy as imposed by a large country. No imports are permitted.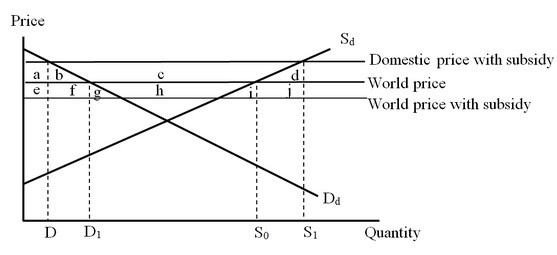 What is the net impact on the producer surplus of the export subsidy provided by the domestic government?
What is the net impact on the producer surplus of the export subsidy provided by the domestic government?
A. The producer surplus increases by area (a + b + c).
B. The producer surplus increases by area (a + b + c + d).
C. The producer surplus falls by area (a + b).
D. The producer surplus falls by area (a + b + c + e + f + g + h).
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
When the bandwagon effect exists, a change in price is likely to
A) change total revenue less than if there were no network externalities. B) change total revenue more than if there were no network externalities. C) change total revenue the same amount as if there were no network externalities. D) not change total revenue at all.
Consider two goods-one that generates external benefits and another that generates external costs. A competitive market economy would tend to produce: a. too much of both goods, relative to the social optimum
b. too little of both goods, relative to the social optimum. c. too much of the good that generates external benefits relative to the social optimum, and too little of the good that generates external costs. d. too little of the good that generates external benefits relative to the social optimum, and too much of the good that generates external costs.
A firm that attempts to pass along the cost of higher union wages to consumers in the form of higher prices will be more successful if the price elasticity of demand for its product is
A. Elastic. B. Unitary. C. Inelastic. D. Perfectly elastic.
Which of the following best approximates a pure monopoly?
A. The Kansas City wheat market B. The only bank in a small town C. The soft drink market D. The foreign exchange market