The difference between a private good and a public good is that
A. private goods are government-sponsored goods while public goods are government-inhibited goods.
B. private goods make us happy while public goods do not.
C. externalities are always created in the production process but not in the production of public goods.
D. the exclusion principle applies to a private good but not to a public good.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The line that relates the price of a good and the quantity demanded of that good is called the demand
a. schedule, and it usually slopes upward. b. schedule, and it usually slopes downward. c. curve, and it usually slopes upward. d. curve, and it usually slopes downward.
If the interest rate is 5 percent and cash flows are $3,000 at the end of year one and $5,000 at the end of year two, then the present value of these cash flows is:
A. $8,400.34. B. $400.74. C. $7,392.29. D. $4,222.50.
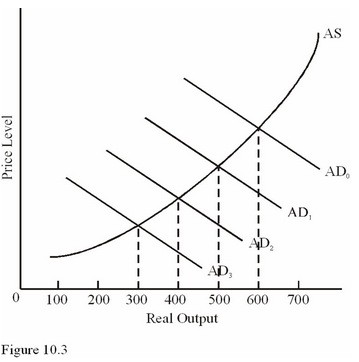 Refer to Figure 10.3. If autonomous investment spending drops by enough to shift the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2, the multiplier effect is likely to
Refer to Figure 10.3. If autonomous investment spending drops by enough to shift the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2, the multiplier effect is likely to
A. Create a second induced shift from AD2 to AD3. B. Create a second induced shift from AD2 back to AD1. C. Have no effect on the AD curve. D. Create a second induced shift from AD2 to AD0.
Refer to the graph below. At equilibrium, the producer surplus would be represented by the area:
The equilibrium point in the market is where S and D curve intersect.
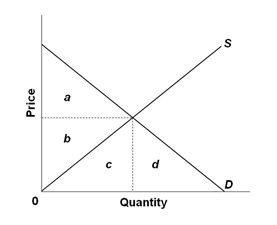
A. b
B. b + c
C. a + b
D. b + c + d