Player 1 and Player 2 are playing a game in which Player 1 has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Player 1 has chosen either Up or Down, Player 2, who can see what Player 1 has chosen, must choose Up or Down at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch.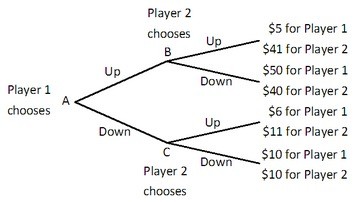 What is the equilibrium outcome of this game?
What is the equilibrium outcome of this game?
A. Player 1 and Player 2 both choose Down.
B. Player 1 chooses Up and Player 2 chooses Down.
C. Player 1 chooses Down and Player 2 chooses Up.
D. Player 1 and Player 2 both choose Up.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Tom takes 20 minutes to cook an egg and 5 minutes to make a sandwich. Jerry takes 15 minutes to cook an egg and 3 minutes to make a sandwich. If Tom and Jerry trade
A) Tom will benefit and Jerry will not. B) Jerry will benefit and Tom will not. C) both will benefit. D) none of them will benefit.
The corporate income tax is ultimately paid by all of the following except
A) owners of the corporation. B) the corporation's debtors in the form of lower rates of return on the corporation's bonds. C) employees in the form of lower wages. D) customers in the form of higher prices.
Which of the following is a disadvantage of the corporation compared to the sole proprietorship?
a. limited liability b. difficulty raising start-up money c. lack of profitability d. corporate income is taxed twice e. corporations are more vulnerable in the case of the death of an owner
Just like models constructed in other areas of science, economic models
a. incorporate assumptions that contradict reality. b. incorporate all details of the real world. c. complicate reality. d. avoid the use of diagrams and equations.