Refer to the information provided in Figure 29.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.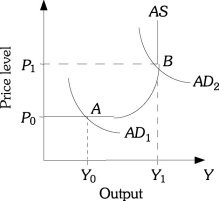 Figure 29.2Refer to Figure 29.2. If economic policy causes aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD1, then
Figure 29.2Refer to Figure 29.2. If economic policy causes aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD1, then
A. output decreases to less than Y1.
B. the price level decreases lower than P0 and output decreases to Y0.
C. output decreases to Y0 and the price level decreases to P0.
D. none of the above.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
A monopoly firm's demand curve
A) is more inelastic than the demand curve for the product. B) is inelastic at high prices and elastic at lower prices. C) is perfectly inelastic. D) is the same as the market demand curve.
Suppose that for Jim the marginal benefit (MB) of producing is $60 and that the marginal cost (MC) of producing is $10. Suppose also that his marginal benefit of stealing is $50 and the marginal cost of stealing is $10. Is Jim currently maximizing utility in terms of producing and stealing? If not, should he produce more and steal less, or produce less and steal more to move toward utility maximization?
A. Yes, Jim is maximizing utility. B. No, Jim is not maximizing utility. Since the MB/MC ratio for producing is less than the MB/MC ratio for stealing, Jim should produce more and steal less. C. No, Jim is not maximizing utility. Since the MB/MC ratio for producing is greater than the MB/MC ratio for stealing, Jim should produce more and steal less. D. No, Jim is not maximizing utility. Since the MB/MC ratio for producing is greater than the MB/MC ratio for stealing, Jim should steal more and produce less.
Those who believe in the rational expectations hypothesis advocate
A. active fiscal policy during recessions. B. active monetary policy during inflationary periods only. C. no policy intervention. D. active monetary policy during recessions.
The following economy produces two products.ProductsProduction Possibilities?ABCDEFSteel012345Wheat100907555300Refer to the above table. The total opportunity cost of the three units of steel is:
A. 45 units of wheat. B. 15 units of wheat. C. 20 units of wheat. D. 55 units of wheat.