Series/Parallel Circuits: What is the potential drop from point A to point B for the circuit shown in the figure? The battery is ideal, and all the numbers are accurate to two significant figures.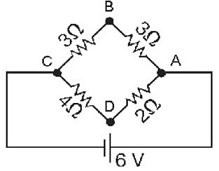
A. 0.35 V
B. 2.0 V
C. 2.5 V
D. 3.0 V
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Does the uncertainty principle affect our ability to follow the path of a baseball? Why or why not?
A) No, because the uncertainties in the position and momentum of the baseball are so small in comparison to its size and total momentum that they are unnoticeable. B) Yes, because we cannot know both where the baseball is and which way it is going at the same time. C) No, because the exclusion principle says that large objects are excluded from the consequences of the uncertainty principle. D) No, because the uncertainty principle applies only to electrons.
Molecular Speeds: If the temperature of a gas is increased from 20°C to 100°C, by what factor does the rms speed of an ideal molecule change?
A. 1.1 B. 1.3 C. 2.2 D. 1.6
What is the reason cities buy water rights from farmers? Is this a good or a poor way to address the problems?
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is a key factor in explaining why many jovian moons have been more geologically active than the Moon or Mercury?
A) Jovian moons contain much more ice that can melt or deform at lower temperatures than can the rock and metal that make up the Moon and Mercury. B) The jovian moons are considerably larger than the Moon and Mercury and therefore have retained much more internal heat. C) The jovian moons probably have far more internal heat generated by radioactive decay than do the Moon or Mercury. D) Because of their greater distances from the Sun, the jovian moons receive much less heat from the Sun.