The manager of a perfectly competitive firm has to decide:
A) the quantity of output the firm should produce.
B) the price the firm should charge for its output.
C) the quantity of output the firm should produce and the price it should charge.
D) neither the quantity of output the firm should produce nor the price it should charge because the market makes both of these decisions.
A
You might also like to view...
If you believe that expectations react quickly, you are likely a
A. believer in rational expectations. B. Keynesian. C. theoretical economist. D. None of the above is correct.
The yardstick most often used to compare living standards across nations is
a. average production cost per unit b. sales revenue per month c. utility per capita d. GDP per person e. imports per year
If television sellers expect the prices of televisions to fall in the future, we are likely to see the price:
A) of televisions fall and quantity of televisions rise. B) of televisions rise and quantity of televisions fall. C) and quantity of televisions fall. D) and quantity of televisions rise.
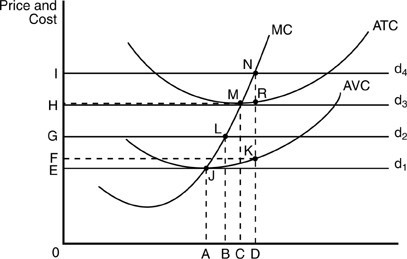 If the firm in the above figure produces output level D, it incurs an average fixed cost of production equal to the distance
If the firm in the above figure produces output level D, it incurs an average fixed cost of production equal to the distance
A. KR. B. DK. C. RN. D. JL.