A risk-averse person has
a. utility and marginal utility curves that slope upward.
b. utility and marginal utility curves that slope downward.
c. a utility curve that slopes down and a marginal utility curve that slopes upward.
d. a utility curve that slopes upward and a marginal utility curve that slopes downward.
Ans: d. a utility curve that slopes upward and a marginal utility curve that slopes downward.
You might also like to view...
For a firm that uses land, labor and capital as inputs, how should the inputs be utilized in order to minimize total costs?
What will be an ideal response?
The rational expectations hypothesis is a theory that states that
A. people make their economic plans by relying on the policy statements made by the President and by leaders in Congress. B. individuals can predict the future perfectly, at least with respect to macroeconomic variables like the interest rate and inflation. C. people make their economic plans by using all available past and present information and their understanding about how the economy operates. D. people make their economic plans in an irrational, intuitive manner.
A research project is conducted by offering a randomly selected 300 of the 500 local Toyota Prius owners a chance to use a new fuel additive for 6 months to see if their gas mileage improves. 225 of the 300 randomly selected Prius owners agree to the offer, 50 of those drop out of the project after 1 month, another 50 drop out after 2 months, and 25 more drop out after 3 months. The rest remain for the duration of the project. Using the intention to treat method, the results from how many of the Prius owners who were randomly selected should be included in the research project?
A. 100 B. 200 C. 225 D. 300
Refer to the figures. If government policy can be used to affect the level of demand in the economy, these figures suggest that government policy:
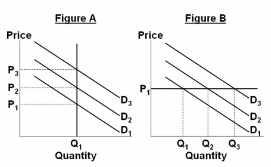
A. can affect the level of output in the very short run, when prices are stuck.
B. can affect the level of output in the longer run, when prices are flexible.
C. cannot affect output in either the very short run or the longer run.
D. can be used to simultaneously affect the levels of output and prices.