Define the terms recessionary gap and inflationary gap. Why do they occur?
A recessionary gap exists when the expenditure line cuts the 45-degree line at a level a GDP below the full employment level of output. This means that total spending is not large enough to employ all workers in the economy who are willing and able to work at current wage levels. An inflationary gap exists when the level of total spending is greater than the potential output of the economy. This means that all workers are fully employed and increases in production are not possible on a sustained long-run basis. The usual result of an inflationary gap is an increase in the price level, hence the name of the condition.
You might also like to view...
GDP divided by the population gives us
A) the price level. B) the GDP deflator. C) per capita GDP. D) real GDP. E) none of the above.
Combating the "greenhouse effect" has classic free-rider problems
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Answer the following questions true (T) or false (F)
1. If a perfectly competitive firm maximizes short-run profits, its marginal revenue will be positive and less than its price. 2. A profit-maximizing monopolistically competitive firm produces and sells an allocatively efficient quantity of output. 3. Unlike a perfectly competitive firm, a monopolistic competitor does not have a short-run shut-down point.
Refer to the graph shown. If the government imposed a price ceiling of $4, the quantity purchased by consumers in this market would: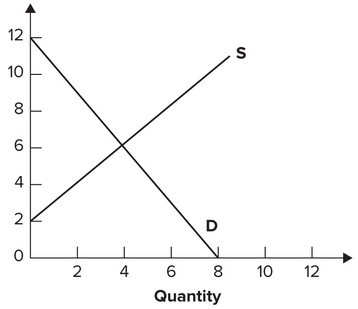
A. increase from 4 to 6. B. decline from 6 to 4. C. increase from 2 to 4. D. decline from 4 to 2.