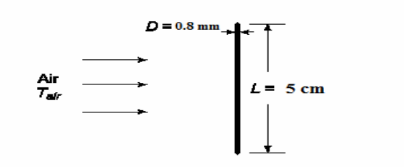
A copper wire, 0.8 mm OD, 5 cm long, is placed in an air stream whose temperature rises at a rate given by Tair = (10+ 14t)°C, where t is the time in seconds. If the initial temperature of the wire is 10°C, determine its temperature after 2 s, 10 s and 1 min. The heat transfer coefficient between the air and the wire is 40 W/(m2 K).
GIVEN
• A copper wire is placed in an air stream
• Wire diameter (D) = 0.8 mm=8*10-4 m
• Wire length (L) = 5 cm=0.05 m
• Air stream temperature is: Tair = (10 + 14t)°C
• The initial temperature of the wire (To) = 10°C
• The heat transfer coefficient ( )ch = 40 W/(m2 K)
FIND
• The wire temperature after 2 s, 10 s and 1 min
ASSUMPTIONS
• Constant and uniform heat transfer coefficient
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
For copper at 127°C
• Thermal conductivity (k) = 383 W/(m K)
• Density (?) = 8933 kg/m3
• Specific heat (c) = 383 J/(kg K)
The Biot number for this problem is
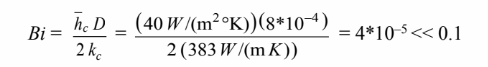
Therefore the internal resistance of the wire can be neglected.
The temperature-time history of the wire can be calculated from the energy balance,
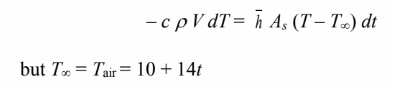
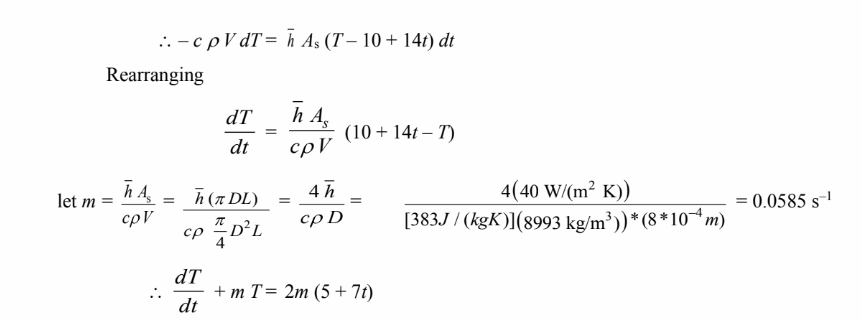
This is a linear, first order, non-homogeneous differential equation with a homogeneous solution of T = c e–mt and a particular solution T = co + c1 t. Therefore, the general solution has the form:
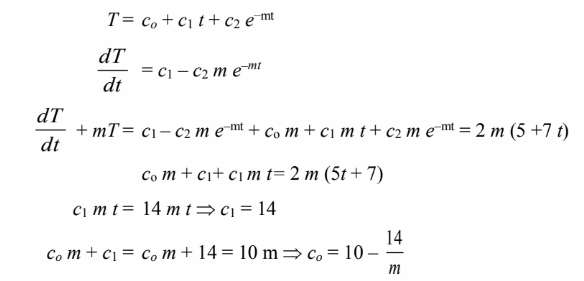
Substituting these back into the assumed solution yields
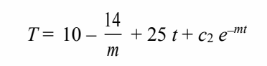
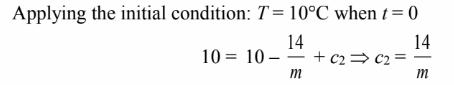
Therefore, the temperature-time history of the wire is
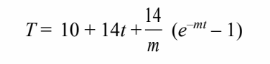
Evaluating the wire temperature at the requested times
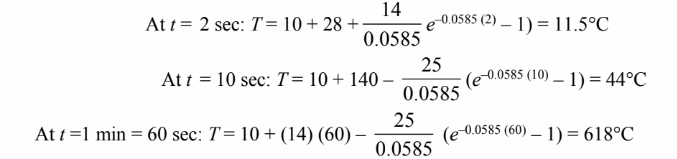
You might also like to view...
In the context of astronomy, a habitable zone is:
A) a region on a planet where conditions are acceptable for life to exist. B) a region around a star where a planet's temperature would permit the existence of liquid water. C) a region on a young planet where amino acids can begin to form deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules. D) a region around a star where different types of planets can form.
What is one idea why a relatively dense protogalactic cloud more likely to produce an elliptical galaxy than a spiral galaxy?
A) The force of gravity from the higher gas density can pull the material into a more spherical shape. B) The more frequent collisions between particles in the high-density gas randomize the particle orbits. C) The thickness of the dense cloud prevents a disk from forming. D) The higher gas density allows more rapid star formation, leaving little gas to form a disk.
From the center out, the correct order of the parts of the Sun is
A. radiative zone, core, chromosphere, convection zone, photosphere, corona. B. core, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona, radiative zone. C. core, radiative zone, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona. D. core, convection zone, radiative zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona.
Thermal energy is measured in
A) calories. B) Calories. C) joules. D) any or all of the above for special cases