The equilibrium compensating wage differential between two occupations in the same city is $10 per hour. Both occupations have equivalent training requirements. Shannon works in the higher-paying occupation and would have been willing to do so even if the compensating differential was $5 per hour. Therefore,
a. Shannon will migrate to the lower-paying occupation
b. Shannon must have a greater distaste than the typical worker for the nonmonetary characteristics of her occupation
c. the equilibrium compensating wage differential is more than enough to prevent Shannon from moving to the other job
d. the higher-paying occupation cannot have a perfectly competitive labor market
e. Shannon must have a greater preference than the typical worker for the lower- paying occupation
C
You might also like to view...
If national saving (S) is $100,000, net taxes (T) equal $100,000 and government expenditure (G) is $25,000, how much are households and businesses saving?
A) $25,000 B) $225,000 C) -$25,000 D) none of the above
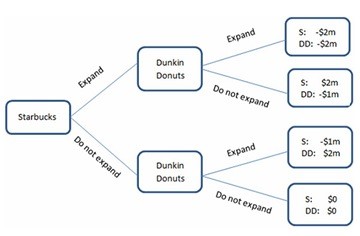 This figure displays the choices being made by two coffee shops: Starbucks and Dunkin Donuts. Both companies are trying to decide whether or not to expand in an area. The area can handle only one of them expanding, and whoever expands will cause the other to lose some business. If they both expand, the market will be saturated, and neither company will do well. The payoffs are the additional profits (or losses) they will earn.The outcome of the game in the figure shown will be:
This figure displays the choices being made by two coffee shops: Starbucks and Dunkin Donuts. Both companies are trying to decide whether or not to expand in an area. The area can handle only one of them expanding, and whoever expands will cause the other to lose some business. If they both expand, the market will be saturated, and neither company will do well. The payoffs are the additional profits (or losses) they will earn.The outcome of the game in the figure shown will be:
A. Starbucks will expand and Dunkin Donuts will not. B. Starbucks and Dunkin Donuts will both expand. C. Starbucks will not expand and Dunkin Donuts will. D. neither Starbucks nor Dunkin Donuts will expand.
Which of the following is true of interest-rate risk?
A. It refers to the probability that a borrower will default on debt obligations. B. It is the risk that the coupon rate for a bond will change, affecting current bondholders' coupon payments. C. Individuals owning long-term bonds are exposed to greater interest-rate risk. D. It is the risk that the face value of a bond will change before maturity.
In September 2005, destruction to U.S. gasoline refineries was caused by back-to-back storms along the U.S. Gulf Coast—Hurricane Katrina and Hurricane Rita. In one week, the average price of a gallon of gasoline in the United States increased by about
40 cents. Which of the following best explains why these events pushed up the price of gasoline? A) The demand curve for gasoline shifted to the left along the supply curve for gasoline. B) The supply curve for gasoline shifted to the left along the demand curve for gasoline. C) The demand curve for gasoline shifted to the right along the supply curve for gasoline. D) The supply curve for gasoline shifted to the right along the demand curve for gasoline.