Refer to Price Ceiling. After the price ceiling is imposed, consumers' surplus is equal to
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram which shows the effects of a price ceiling. The initial price and quantity are P0 and Q0, respectively, and the price ceiling is imposed at the price P1. Assume that none of the potential deadweight loss can be avoided.
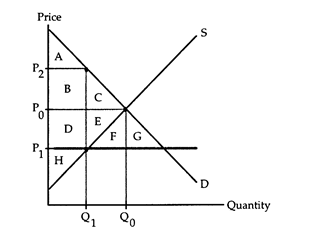
a. area A.
b. area A + B.
c. area A + B + D.
d. area A + B + C + D + E + F + G.
a. area A.
You might also like to view...
According to polling data, Americans believe that after-tax corporate profits are
A. less than 10 percent of corporate product prices. B. nearly 50 percent of the corporate product price. C. approximately 36 percent of corporate product prices. D. approximately 25 percent of corporate product prices.
An exchange rate arrangement with a free market determined floating exchange rate for capital account transactions and a fixed exchange rate for current account transactions is called
A) capital-current account exchange rate system. B) dual exchange rate system. C) managed exchange rate system. D) crawling peg exchange rate system.
Suppose that goods A and B are close substitutes. If the price of good A falls, then we would expect an:
A. Increase in the demand for A and an increase in the quantity of B demanded B. Increase in the demand for A and a decrease in the quantity of B demanded C. Increase in the quantity of A demanded and a decrease in the demand for B D. Increase in the demand for good A as well as for good B
For a linear and downward sloping demand curve, when the consumer has to pay a positive price for the good, the value to the consumer is a
A. rectangle. B. triangle. C. four-sided figure that is a rectangle on the bottom and a right triangle on the top whose hypotenuse is the supply curve. D. four-sided figure that is a rectangle on the bottom and a right triangle on the top whose hypotenuse is the demand curve.