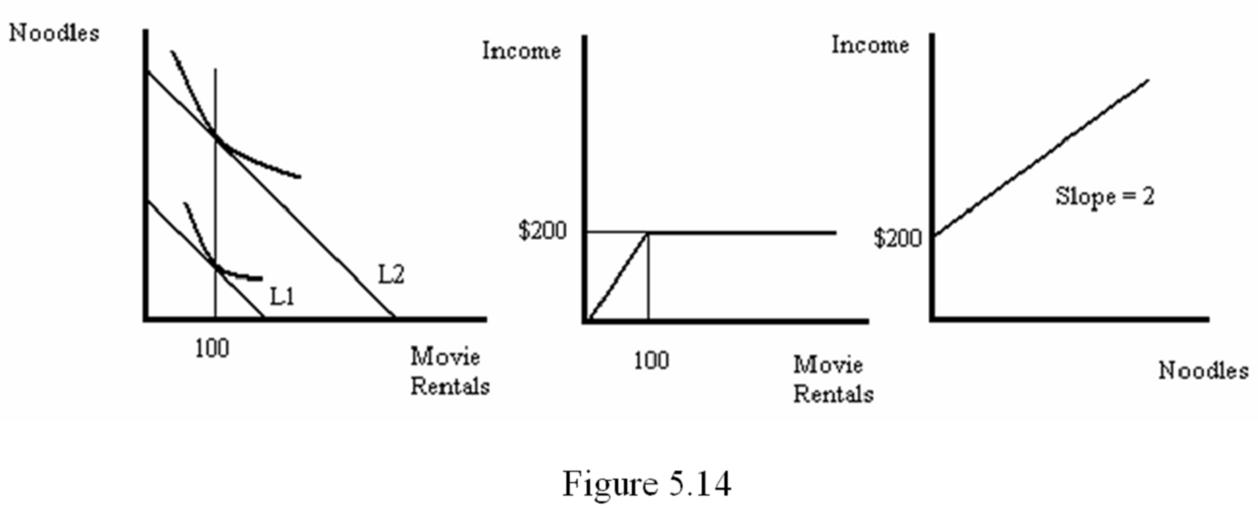
Stewie spends all of his income on movie rentals (R) and noodles (N). His marginal rate of substitution for rentals with noodles is given by MRSRN = 20/?R. Suppose that movies rent for $2 and noodles cost $1. Plot his income-consumption curve, his Engle curve for movie rentals and his Engel curve for noodles.
What will be an ideal response?
Start with the utility maximizing condition 20/?R = PR/PN = $2/$1. Solving for R yields R = 100, implying Stewie spends $200 on movie rentals. That means he spends $2(M-200) on noodles. So, for income levels less than $200, Stewie only rents movies. His income-consumption curve, his Engle curve for movie rentals and his Engel curve for noodles are shown in Figure 5.14.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following correctly identifies a difference between cross-sectional data and time series data?
A. Cross-sectional data is based on temporal ordering, whereas time series data is not. B. Time series data is based on temporal ordering, whereas cross-sectional data is not. C. Cross-sectional data consists of only qualitative variables, whereas time series data consists of only quantitative variables. D. Time series data consists of only qualitative variables, whereas cross-sectional data does not include qualitative variables.
Which of the following countries has the lowest export ratio?
A. Myanmar. B. Belgium. C. Germany. D. The United States.
The table below shows the number of umbrellas and bushels of corn produced in the United Kingdom and the rest of the world per labor hour. The rest of the world has an absolute advantage in the production of ProductivityIn the United KingdomIn the Rest of the WorldUmbrellas per labor hour0.251.00Bushels of corn per labor hour0.500.67
A. only corn. B. neither corn nor umbrellas. C. only umbrellas. D. both goods.
The consumption schedule directly relates:
A. consumption to the level of disposable income. B. saving to the level of disposable income. C. disposable income to domestic income. D. consumption to saving.