Describe how tides affect marine organisms living in the intertidal zone. What will be an ideal response?
The tides have a significant influence on coastal marine life. Within the intertidal zone itself,
organisms are exposed to varying amounts of emergence and submergence. Because some
organisms can tolerate many hours of exposure and others are able to tolerate only a very few
hours per week or month, the animals and plants sort themselves into three or more
horizontal bands, or subzones, within the intertidal zone. Each distinct zone is an aggregation
of animals and plants best adapted to the conditions within that particular narrow habitat.
Examples of animals who live in this area include: the tiny diatom (one-celled alga)
Hantzschia migrates upward through wet sand to photosynthesize at the sunlit surface at low
tide. At the first hint of the returning tide, these plantlike organisms descend to a relatively
safe depth in the sand, where they are protected from wave action. Fiddler crabs return to
their burrows at high tide to avoid marine predators but emerge at low tide to look for any
bits of food. Filter-feeding animals such as sand crabs and bean clams migrate up and down
the beach to stay in the surf zone where the chaos can provide both food and protection.
You might also like to view...
What is considered to be the world's most important marine product?
A) Algin B) Fish C) Seaweed for consumption D) Bycatch
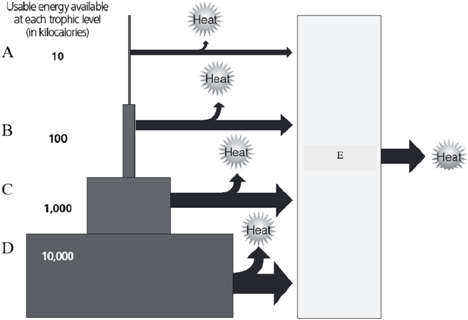
What will be an ideal response?
Which temperature scale was developed first?
A) Celsius B) Fahrenheit C) Kelvin D) All three were proposed within a year of each other.
________ is the longest barrier island along the coast of the United States.
A) Santa Catalina Island, California B) Martha's Vineyard, Massachusetts C) Mt. Desert Island, Maine D) Fire Island, New York E) Padre Island, Texas