Suppose the target exchange rate set by the Fed is 150 yen per dollar. If the demand for dollars permanently decreases, then the Fed
A) can permanently meet the target by selling dollars.
B) can permanently meet the target by buying dollars.
C) must violate both interest rate parity and purchasing power parity to permanently meet the target.
D) cannot permanently maintain the target rate.
D
You might also like to view...
When the price of a product is increased 10 percent, the quantity demanded decreases 15 percent. The price elasticity of demand for this product is
A. -67. B. -0.67. C. -0.15. D. -1.5.
According to the graph shown, if this economy were to open to trade, which amount of surplus would be transferred?
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good, as well as the world price for that good.
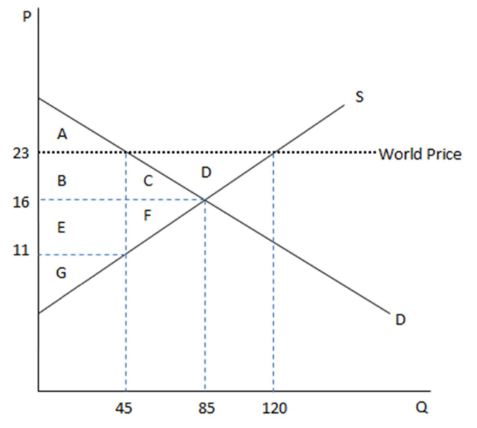
A. Area FG would be transferred to the consumer.
B. Area DE would be transferred to the consumer.
C. Area DEFG would be transferred to the consumer.
D. Area FG would be transferred to the producer.
Susan argues that she is the victim of economic discrimination. The primary technical difficulty for an economist investigating her claim will be
a. defining economic discrimination. b. finding a worker with the same productivity as Susan for comparison purposes. c. defining statistical discrimination. d. measuring Susan's human capital.
Which of the following would be most likely if firms in a competitive price-searcher market were earning economic profit?
a. Production inefficiencies would persist until the profit was eliminated. b. Firms would decrease their rate of output in the short run, causing a decline in profitability in the market. c. New firms would enter the market, resulting in fewer sales by existing firms. d. All firms in the market would continue to produce at their current levels and continue to charge the same price.