As the IS curve becomes flatter, we know that
A) a given change in the money supply will cause a larger change in output.
B) a given change in the money supply will cause a smaller change in output.
C) a given change in the money supply will cause the same change in output.
D) monetary policy becomes less effective.
B
You might also like to view...
Based on this figure, if the official fixed value of krone is fixed at $0.15 per krone, then the Norwegian krone is ________ and the international reserves of Norway will ________ krone per period. 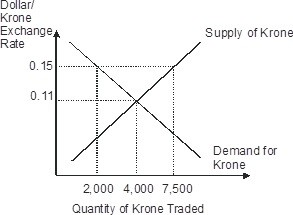
A. undervalued; increase by 2,000 B. undervalued; increase by 5,500 C. overvalued; decrease by 2,000 D. overvalued; decrease by 5,500
The marginal dollar cost to a patient of visiting a doctor when the patient's bill will be paid entirely by insurance is
A) the same as if the patient had no insurance. B) the value of the care not received by some other patient who couldn't get an appointment. C) zero. D) zero only if the patient does not pay the insurance premiums.
The law of diminishing returns results in:
A. an eventually rising marginal product curve. B. a total product curve that eventually increases at a decreasing rate. C. an eventually falling marginal cost curve. D. a total product curve that rises indefinitely.
The price of a first-class stamp in 1957 was 3 cents, and it is 47 cents in 2016. From this we know that
A. the money price of first-class stamps increased from 1957 to 2016, but we can't tell if the relative price of first-class stamps increased or decreased without more information. B. the money price of first-class stamps increased from 1957 to 2016 but the absolute price of first-class stamps stayed constant. C. both the relative and the absolute price of first-class stamps increased from 1957 to 2016. D. the money price of first-class stamps increased from 1957 to 2016 and the relative price of first-class stamps decreased.