Define the following terms or concepts:
a. Law of electroneutrality
b. Normality
c. Equivalent
d. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
e. Total Suspended Solids (TSS)
f. Volatile Suspended Solids (VSS)
g. Fixed Solids
h. Total Hardness
i. Carbonate Hardness
j. Noncarbonated Hardness
k. Chemical Reactivity
l. Chemical Activity
m. Standard State Activity
n. Activity Coefficient
o. Solubility
p. Precipitate
q. Reduction–Oxidation Process
r. Ionic Reaction
s. Dissolution Salts
t. Sorbent
u. Sorbate
a. Law of electroneutrality- states that the sum of all positive ions (cations) in solution must equal the sum of all the negative ions (anions) in solution, so that the net charge of all natural waters is equal to zero: ?cations - ?anions = 0
b. Normality- of a solution is the number of equivalents per liter, and can be determined by multiplying the concentration of a specie, , by the number of equivalents, 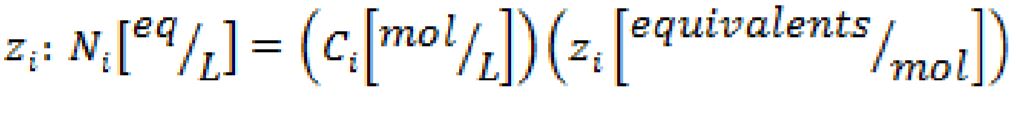
c. Equivalent- means that the number of charge equivalents (eq) associated with a compound is equal to the absolute value of the charge associated with the form of the dissolved ion. (example: the dissolved sodium ion, Na+, has a charge of +1 or 1 equivalent)
d. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)- consist of salts and minerals that have been dissolved through natural weathering of soils or through the anthropogenic process
e. Total Suspended Solids (TSS) - the materials that are floating or suspended in the water
f. Volatile Suspended Solids (VSS) - determined by the weight of any particles that have evaporated from a filter after the filter is heated to 550oC
g. Fixed Solids - determined by the weight of any particles remaining on a filter heated to 550oC
h. Total Hardness - the sum of the concentration of the divalent cations (species with a charge of 2+) in water
i. Carbonate Hardness - represents the portion of the diprotic ions that can combine with carbonates to form scaling
j. Noncarbonated Hardness - the difference between total hardness and carbonate hardness
k. Chemical Reactivity - the chemical’s overall tendency to participate in a reaction
l. Chemical Activity - a standardized measure of chemical reactivity within a defined system
m. Standard State Activity - Reference state of chemical reactivity
n. Activity Coefficient - used to relate the standard chemical activity and the conditional chemical reactivity
o. Solubility - the amount of a substance that can be dissolved into solution by a solvent
p. Precipitate – The resulting solid form of a substance that forms from oversaturated concentrations in solution
q. Reduction–Oxidation Process - occur when the oxidation state of participating atoms change
r. Ionic Reaction - there is a change in ion–ion interactions and relationships
s. Dissolution Salts - the process of a substance dissolving in solution
t. Sorbent - the material into or onto which the sorbate is transferred
u. Sorbate - the substance that is transferred from one phase to another
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is a true statement?
A. A low pressure A/C cutout switch may prevent A/C compressor operation in extreme cold ambient temperatures. B. A low pressure A/C cutout switch may prevent A/C compressor operation if there is insufficient refrigerant in the system. C. A high pressure A/C cutout switch may prevent A/C compressor operation if the air flow through the condenser is restricted. D. All of the above are true statements.
Explain why loading and unloading livestock are particularly dangerous
What will be an ideal response?
Customer resistance to biotech food products appears to be diminishing, both in the United States and in other nations
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.What feature is an additional function of many memory seat systems that moves the seat rearward when the key is removed from the ignition switch?
What will be an ideal response?