A bond is:
A. a financial asset that represents partial ownership of a company.
B. a payment made periodically to all shareholders of a company.
C. an agreement in which a lender gives money to a borrower in exchange for a promise to repay the amount loaned plus an agreed-upon amount of interest.
D. a promise by the bond issuer to pay a lump sum at a specified maturity date, and, in some cases, to pay periodic interest at a specific percentage rate.
D. a promise by the bond issuer to pay a lump sum at a specified maturity date, and, in some cases, to pay periodic interest at a specific percentage rate.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 11.2. Suppose that Ca = 40, MPC = 0.8, I = 10. The slope of the consumption function is
A) 0.1. B) 0.2. C) 0.8. D) 0.9.
If the United States is experiencing inflation, then it will be most willing to engage in international policy coordination that requires:
A. expansionary U.S. monetary policy. B. strengthening the dollar. C. weakening the dollar. D. expansionary U.S. fiscal policy.
The more bowed out the Lorenz curve, the
A) less equal the income distribution. B) more equal the income distribution. C) greater the overall wealth in the economy. D) less the overall wealth in the economy.
Refer to the diagram. The combination of computers and bicycles shown by point F:
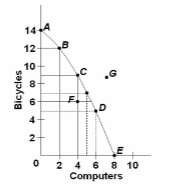
A. is unattainable given currently available resources and technology.
B. is attainable but implies that the economy is not using all its resources.
C. is irrelevant because it is inconsistent with consumer preferences.
D. suggests that opportunity costs are constant.