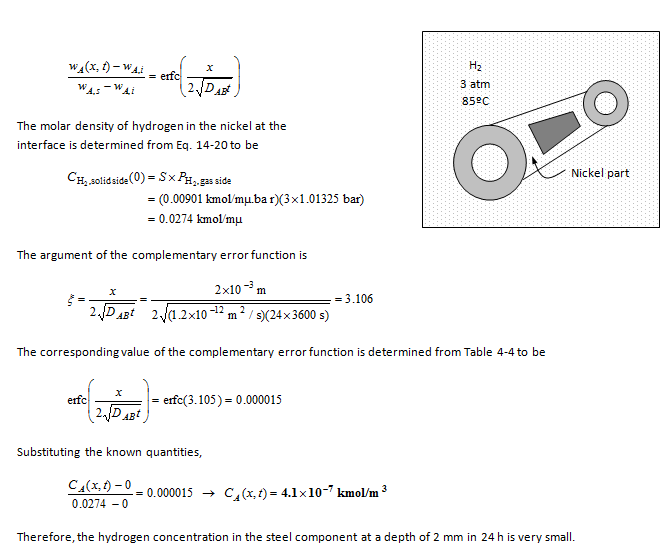
A thick part made of nickel is put into a room filled with hydrogen at 3 atm and 85°C. Determine the hydrogen concentration at a depth of 2 mm from the surface after 24 h.
What will be an ideal response?
A nickel part is put into a room filled with hydrogen. The ratio of hydrogen concentrations at the surface of the part and at a depth of 2-mm from the surface after 24 h is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Hydrogen penetrates into a thin layer beneath the surface of the nickel component, and thus the component can be modeled as a semi-infinite medium regardless of its thickness or shape. 2 The initial hydrogen concentration in the nickel part is zero.
Properties The molar mass of hydrogen H2 is M = 2 kg/kmol (Table A-1). The solubility of hydrogen in nickel at 358 K (=85ºC) is 0.00901 kmol/m³.bar (Table 14-7). The mass diffusivity of hydrogen in nickel at 358 K is DAB =1.2?10-12 m2/s (Table 14-3b). Also, 1 atm = 1.01325 bar.
Analysis This problem is analogous to the one-dimensional transient heat conduction problem in a semi-infinite medium with specified surface temperature, and thus can be solved accordingly. Using mass fraction for concentration since the data is given in that form, the solution can be expressed as
You might also like to view...
A lamp outage module can monitor the operation of which lighting system?
A. Headlights B. Taillights C. Stoplights D. All of the above
Describe why world views are useful when programming CNC machines.
What will be an ideal response?
A radio receiver has an input resistance of 300 ?. When it is connected directly to an antenna system with a characteristic impedance of 75 ?, an impedance mismatch occurs. By inserting an impedance-matching transformer ahead of the receiver, maximum power can be realized. Calculate the required turns ratio.
What will be an ideal response?
Which alignment angle is most likely to need correction and cause the most tire wear?
A) Caster B) Camber C) SAI D) Toe