A 3.0-kg mass sliding on a frictionless surface has a velocity of 5.0 m/s east when it undergoes a one-dimensional inelastic collision with a 2.0-kg mass that has an initial velocity of 2.0 m/s west. After the collision the 3.0-kg mass has a velocity of 1.0 m/s east. How much kinetic energy does the two-mass system lose during the collision?
a. 22 J
b. 24 J
c. 26 J
d. 20 J
e. 28 J
b
You might also like to view...
Consider a compass with a square magnet placed in a uniform electric field, as shown below. Supposing that we place the square-magnet compass in a rightward magnetic field 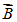 instead of a rightward electric field
instead of a rightward electric field 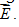 .
.
A. Clockwise, to align itself with the field. B. Counter clockwise, to align itself with the field. C. 180° either clockwise or counter clockwise. D. It won’t turn, as it is already aligned with the field. E. It won’t turn, because the field wants to twist it around a different axis altogether. F. It won’t turn because it is not affected by this field.
The orientation of an image seen projected on a screen by a single lens is always __________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
One kilogram of chilled water at 32°F (0°C) is placed in a freezer which is kept at 0°F (?18°C). Approximately how much electric energy (in kilocalories) is needed to operate the compressor to cool this water to 0°F if the room temperature is maintained at 75°F (24°C)? (Lice = 3.33 × 10^5 J/kg; cice = 2.09 × 10^3 J/kg/°C)
a. 13 b. 1.5 c. 15 d. 16 e. 33
A 60.0 W light bulb radiates light uniformly in all different directions. What is the value of E at a distance of 0.400 m from the bulb?
A) 162 N/C B) 212 N/C C) 82.1 N/C D) 106 N/C E) 52.9 N/C