Sectoral changes in demand
a. create frictional unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to attract a better pool of candidates creates structural unemployment.
b. create structural unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to attract a better pool of candidates creates frictional unemployment.
c. and firms paying wages above equilibrium to attract a better pool of candidates both create structural unemployment.
d. and firms paying wages above equilibrium to attract a better pool of candidates both create frictional unemployment.
a
You might also like to view...
The table above gives Jane's total utility from magazines and CDs. The price of a magazine is $4 and the price of a CD is $10. If Jane's total budget for magazines and CDs is $70.00 per week, what is her total utility at her utility maximizing consumer equilibrium?
A) 2480 units B) 1870 units C) 210 units D) 30 units
The object of inflation targeting is for a country's central bank to try to keep the inflation rate near
A) the country's historical average economic growth rate. B) some predetermined level. C) the country's historical average inflation rate. D) the country's historical average unemployment rate.
According to the classical model, an increase in aggregate demand would
A. raise real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) but leave the price level unchanged. B. lead the economy to recession. C. lead the economy to a deflationary cycle. D. cause an adjustment to a higher price level.
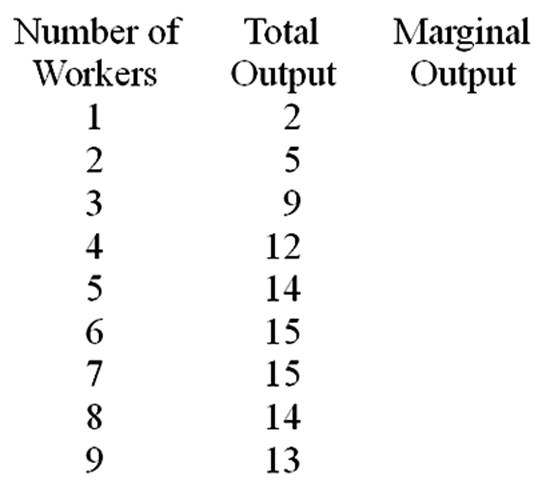
Fill in the Marginal Output column.