Refer to the figures below to answer this question:
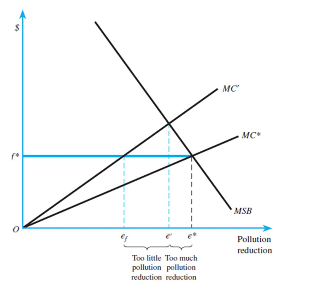
Cap-and-trade versus emissions fee when marginal social benefits are inelastic and costs are
uncertain:
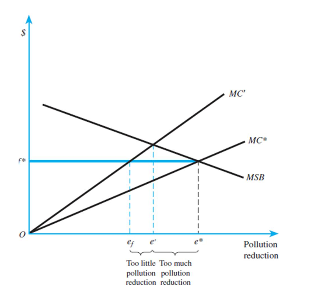
Cap-and-trade versus emissions fee when marginal social benefits are elastic and costs are uncertain:
a) In case of an inelastic marginal social benefit curve, what type of pollution reduction system should the government employ? Why?
b) If the social benefit curve is elastic, do you answer change?
c) What are advantages and disadvantages of Cap-and-Trade systems over Emission Fee
systems when the inflation and change in marginal costs are considered?
a) When the social marginal benefit curve is inelastic then the government should employ a
cap-and-trade system because it is more efficient than the emission fee system. Emission fee
system allows too little pollution compared to fairly higher pollution than efficient quantity of
cap-and-trade system.
b) When the social marginal benefit curve is elastic then the government should employ an
emission fee system because it is more efficient. Cap-and-trade system allows too much
pollution reduction compared to fairly close pollution reduction of emission fee system.
c) Cap-and-Trade systems are superior in high inflation environments since it requires no
legislative or regulatory action in response to inflation. Moreover, emission fee systems are not
appropriate when the marginal cost of pollution reduction is not constant. With emission fee
systems, pollution reduction decreases as marginal costs increase. However with cap-and-
trade systems, pollution reduction is constant as marginal costs increase. Finally if the
government is uncertain about the marginal cost of pollution reduction, then the effective
reduction system depends on the elasticity of marginal social benefits.
You might also like to view...
Should the level of pollution be reduced to zero and if not, then to what level?
What will be an ideal response?
You have eaten two bowls of ice cream at Sundae School Ice Cream store. You consider eating a third. As a rational consumer you should make your choice by comparing
a. the benefits from eating all three bowls of ice cream to how much three bowls of ice cream costs. b. the benefits from eating all three bowls of ice cream to how much one more bowl of ice cream costs. c. the benefits from eating one more bowl of ice cream to how much three bowls of ice cream costs. d. the benefits from eating one more bowl of ice cream to how much one more bowl of ice cream costs.
Chapter 11
What will be an ideal response?
Your roommate tells you she's going to join the gym next week. A week and a half goes by and you ask her how the gym is going, and she tells you she's going to wait until the following week. Your roommate's preferences are:
A. better today than tomorrow. B. mistakes. C. time inconsistent. D. considered bad choices.