Refer to the table above. If planned investment is $18 billion, then at the $660 billion level of disposable income, there will be an:
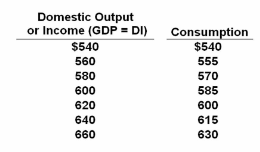
The data below are for a private (no government) closed economy. All figures are in billions of dollars.
A. Unplanned increase in inventories of $12 billion
B. Unplanned increase in inventories of $30 billion
C. Unplanned decrease in inventories of $12 billion
D. Unplanned decrease in inventories of $30 billion
A. Unplanned increase in inventories of $12 billion
You might also like to view...
Which of the following conditions would prevent price discrimination?
a. an economic profit b. a monopoly market structure c. profit maximization d. the inability to identify those customers willing to pay more e. the ability to prevent low-price customers from reselling to high-price customers
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. The purpose of using the four-firm concentration ratio is to calculate how much market share would change in the case of a merger between two of the firms. 2. A minimum price contract is illegal because it would restrict competition. 3. One regulatory option for dealing with natural monopolies is to leave them alone. 4. The purpose of the Dodd-Frank Act was to address numerous accounting scandals involving prominent corporations such as Enron, Tyco International, and WorldCom that occurred as a result of deregulation. 5. If firms were required to pay the social costs of pollution, they would create less pollution but produce less of the product and charge a higher price.
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 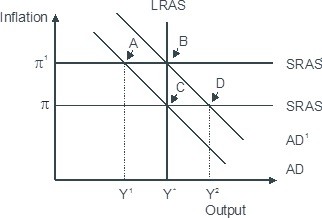
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
Which of the following tools of monetary policy is used least often?
A) open market operations B) setting the required reserve ratio C) setting the discount rate D) acting as a lender of last resort