We assume that in the short run in a perfectly competitive market firms:
A. can enter and exit the market.
B. can exit, but not enter the market.
C. cannot enter or exit the market.
D. can enter, but not exit the market.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
On the graph for a monopolist’s losses, the firm suffers a total loss of ______.
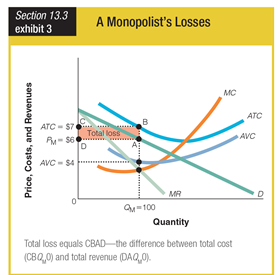
a. $7
b. $100
c. $600
d. $700
When a credit card company offers different services with its card, like travel insurance for air travel tickets purchased with the credit card or product insurance for items purchased with the card, the credit card company is trying to:
A. create a barrier to entry for competing firms. B. create a perfectly competitive market in which to sell its credit card. C. differentiate its credit card from those offered by other companies. D. shift the demand curve for competing firms to the right.
Which of the following will NOT occur when a tariff is imposed on an imported product?
A. The price paid by consumers will rise. B. The price received by importers will fall. C. The level of imports will fall. D. The demand curve for imports will shift to the left.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. Arbitrage refers to the buying and selling activities that cause an equalization of the rates of return on assets that have substantially different characteristics. 2. If investors have two identical assets that have different rates of return, the investors will sell the asset with the higher rate of return to buy the asset with the lower rate of return. 3. Arbitrage activities will make the price of the asset with the higher initial return increase, while the price of the asset with the lower return will decrease. 4. Risk in financial economics refers mainly to the chance that an investment could lose value. 5. Diversification is an investment strategy that seeks to reduce the overall risk in an investment portfolio by selecting a group of assets whose risks differ from one another.