Explain how the decision by parents to not immunize their children, hoping that their children will not get sick because other parents have had their children immunized, is an example of free riding
How is this behavior dangerous to the public and therefore not socially optimal?
Free riding is benefitting from a good without paying for it. Parents who do not get their children immunized because they assume their children will not get sick because all the other children that their children are in contact with have been immunized, are attempting to benefit from the vaccinations of the other children without paying for their own children's vaccinations. This behavior is dangerous to the public because the likelihood of an unvaccinated child catching and spreading a disease is much greater than that of a child who has been vaccinated.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is likely to be true according to Okun's Law?
A) The unemployment rate remains constant when the growth rate of real GDP is 0%. B) The unemployment rate remains constant when the growth rate of real GDP is 3%. C) The unemployment rate increases when the growth rate of real GDP is above 3%. D) The unemployment rate declines when the growth rate of real GDP is below 3%.
Production functions A and B result in the same average total costs of production. However, production function A is twice as capital intensive as production function B. In this case, all else constant:
A) marginal costs will be higher in A than they are in B. B) marginal costs will be higher in B than they will in A. C) because total costs are equal, marginal costs will be equal for the two production functions as well. D) there is no way to say anything about the relative marginal costs of production in the two production functions without additional information.
Oligopolies can result from any of the following EXCEPT
A. government regulation. B. economies of scale. C. vertical mergers. D. diseconomies of scale.
Refer to the information provided in Table 20.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.
Table 20.2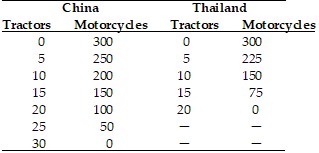 Refer to Table 20.2. In China, the opportunity cost of
Refer to Table 20.2. In China, the opportunity cost of
A. a motorcycle is 1/30 of a tractor. B. a tractor is 10 motorcycles. C. a motorcycle is 10 tractors. D. a tractor is 1 motorcycle.