Figure 14-5
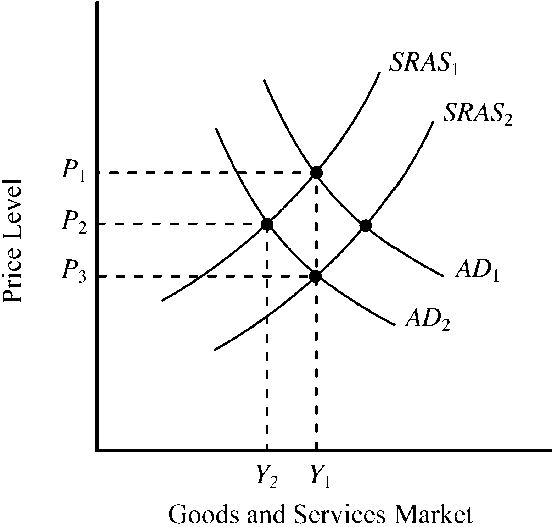
In , AD1 and SRAS1 indicate an economy initially operating at full-employment output level, Y1. The long-run impact of the Fed unexpectedly shifting to a more restrictive monetary policy will be
a.
a decrease in aggregate demand to AD2 and a decrease in real output to Y2.
b.
a decrease in the full-employment level of output to Y2.
c.
a decrease in aggregate demand to AD2 and an increase in short-run aggregate supply to SRAS2, causing the price level to fall to P3 and real output to remain unchanged at Y1.
d.
no change; AD and SRAS will stay at AD1 and SRAS1.
c
You might also like to view...
As the manager of a hotel, you recently noticed that one of your suppliers has started advertising their prices and has changed the specifications of its product to match those of its rivals. The actions of your supplier suggest that any of the following might be occurring except which one?
A) The supplier is attempting to increase its profits. B) The supplier is part of a cartel. C) The supplier is paying treble damages. D) The supplier is attempting to engage in tacit collusio
Suppose you only consume rice and bananas. Can both of these goods be Giffen goods in your consumption?
A) Yes, this is possible B) No, at least one of the goods must be normal C) No, they both can be inferior, but at least one of the goods cannot be a Giffen good D) We need more information about the goods to answer this question
________ inflation is more stable than __________ inflation, because it ____________.
A. Core; headline; excludes food and gasoline prices B. Headline; core; excludes food and gasoline prices C. Core; headline; does not exclude food and gasoline prices D. Headline; core; does not exclude food and gasoline prices
After a particular loan has been paid off, neither the borrower nor the lender has lost purchasing power. Therefore, it must be true that actual inflation was
a. greater than expected inflation. b. equal to expected inflation. c. less than expected inflation. d. greater than the nominal rate of interest.