A conclusion of the theory of rational expectations is that, in the short run, the impact of a correctly anticipated fiscal policy designed to decrease AD will:
a. result in no net change in AD once people's expectations adjustments have been accounted for
b. shift AD in the opposite direction intended once people's expectations adjustments have been accounted for.
c. decrease the price level.
d. result in no change in the price level.
c
You might also like to view...
Refer to Game Matrix II. When would the upper left-hand corner be the likely outcome of this game?
Game Matrix II
The following questions refer to the game matrix below. Player A can play the strategies "High" and "Low," and Player B can play the strategies "Odd" and "Even."
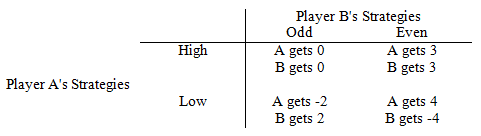
a. When the game is played sequentially, with A being the first player.
b. When the game is played sequentially, with B being the first player.
c. When the players choose their strategies simultaneously.
d. The upper left-hand corner would never be the likely outcome, because the upper right-hand corner makes both player better off.
Suppose firms in a perfectly competitive market are incurring an economic loss. As firms exit, the price ________ and the economic loss of the surviving firms ________
A) rises; increases B) rises; decreases C) falls; increases D) falls; decreases
Which of the following economic systems abolishes all private property?
a. communism b. socialism c. fascism d. All of these.
The competitive price-taker model is usually used to illustrate the competitive process. If firms cannot choose their price, where is the competition?