Refer to the graph shown.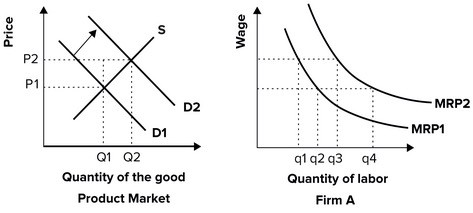 If product demand increases from D1 to D2, the equilibrium price of the product will:
If product demand increases from D1 to D2, the equilibrium price of the product will:
A. increase from P1 to P2 and equilibrium quantity will increase from Q1 to Q2.
B. increase from P1 to P2 and equilibrium quantity will decrease from Q2 to Q1.
C. decrease from P2 to P1 and equilibrium quantity will decrease from Q2 to Q1.
D. decrease from P2 to P1 and equilibrium quantity will increase from Q1 to Q2.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Say's law explains
A) how long-run real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) stability is achieved in the Keynesian model. B) why economies experience business cycles. C) how the economy can go into recession. D) how long-term real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) stability is achieved in the classical model.
What three real-world complications keep purchasing power parity from being a complete explanation of exchange rate fluctuations in the long run? Explain
What will be an ideal response?
The interest rate you typically earn on a deposit at a bank:
A. represents the price of your loan. B. represents the risk of investing. C. is the opportunity cost to you of lending money. D. is the opportunity cost to a bank of lending money.
As a result of advertising prices in monopolistic competition, are
a. higher because firms earn economic profits in the long run b. higher because increased output leads to higher production costs per unit c. lower if increased output allows lower average production costs per unit that more than offset the advertising costs d. lower if advertising costs per unit fall as output increases e. higher because advertising shifts each firm's demand curve to the right and make it flatter