In a price system, changes in prices
A) make it difficult for the system to function well.
B) imply that people have made mistakes in the past.
C) signal to everyone in the system what goods are relatively more or less scarce.
D) signal to policy makers what goods should and should not be taxed more.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Use the following saving schedule to answer the next question. 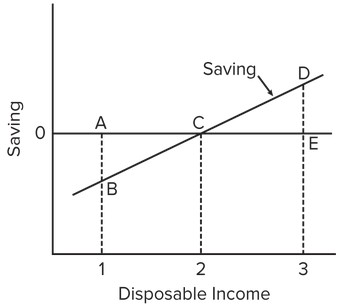 As income falls from level 3 to level 2, the amount of
As income falls from level 3 to level 2, the amount of
A. dissaving increases. B. saving increases. C. dissaving decreases. D. saving decreases.
The curve that reflects the view that when tax rates are too high, lowering them not only creates greater incentive for suppliers to increase production, but ends up generating higher tax revenues, is known as the:
a. Phillips curve. b. Laffer curve. c. Engel curve. d. Rational expectations curve. e. consumption curve.
Assume that the government increases spending and finances the expenditures by borrowing in the domestic capital markets. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the real GDP and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables. b. Real GDP rises, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more positive (or less negative). c. Real GDP rises, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more negative (or less positive). d. Real GDP falls, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more negative (or less positive). e. Real GDP and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending remain the same.
Suppose that Cambodia becomes the next popular tourist destination. You notice that hotels, restaurants, and other services cost much less there than in the United States. From the perspective of the U.S. dollar, what would be the real exchange rate of the Cambodian riel?
a) The real exchange rate would be 0. b) The real exchange rate would be 1. c) The real exchange rate would be greater than 1. d) The real exchange rate would be less than 1.