Compare the outlook regarding the use of nuclear power in the United States and globally in each of the following time periods: 1960s, 1980s, and early 21st century
What will be an ideal response?
United States: 1960s: The U.S. government was interested, after World War II, in converting the technology developed for military purposes into civilian uses. The belief was that the cost of generating electricity from nuclear power would be so cheap that it could be used instead of other forms of fuel. The building of nuclear power plants did not begin until the U.S. government limited the legal liability of those corporations and utilities owning the power plants (Price Anderson Act, 1957). Additionally, the U.S. government assumed responsibility for all high-level nuclear waste generated by commercial nuclear power plants. "In the 1960s and early 1970s, utility companies moved ahead with plans for numerous nuclear power plants. By 1975, 53 plants were operating in the United States, producing about 9% of the nation's electricity, and another 170 plants were in various stages of planning of construction." 1970s: By the mid-1970s the future of nuclear power was no longer rosy. Three bills were passed in California in 1976 halting future construction of nuclear power plants unless the waste product problem was solved. Many existing orders for power plants were cancelled. Construction was terminated in some instances. 1980s: The building and operation of nuclear power plants continued to be curtailed. Shoreham was closed after only 32 hours of operation. The citizens in Sacramento, California, voted to close Rancho Seco, which had been operated by the local public utility company. 1990s: In the 1990s the last nuclear power plant under construction was brought online. The present: The outlook is a bit rosier today because of the problems with coal generation and high electrical demand. With the passage of the Energy Policy Act of 2005, there is a possibility of additional nuclear power plants being constructed in the United States.
Globally: Thirty-one nations have nuclear power plants in operation or under construction. "Including those in the United States, the world has a total of 440 operating nuclear plants, with an additional 32 under construction. After the catastrophic accident at Chernobyl in April 1986, nuclear power is being rethought in many countries. Yet the demand for electricity is more robust than ever, and the other means of generating electricity have their own problems."
You might also like to view...
How many square kilometers of habitat would be required to support 5 species?
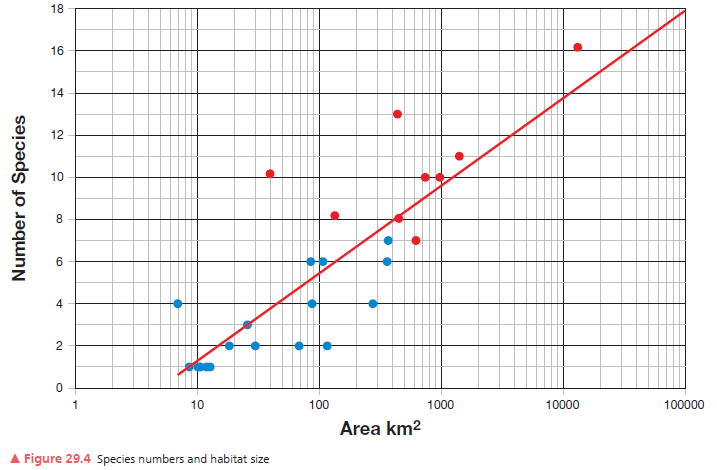
Use Figure 29.4 and the trend line to answer the question.
What apparent difference is there between a gneiss that is formed from igneous rock and one formed from sedimentary rock?
A) crystal size B) mineral content C) age D) color
What are the current impacts of climate change in Europe?
A) Sea ice is dwindling. B) There is sparse snow cover in arctic Scandinavia. C) There are frequent droughts in the water-starved Mediterranean region. D) Dwindling sea ice, and sparse snow cover in arctic Scandinavia.
The increase in financial cost of damages from the Northridge earthquake, as compared to the San Fernando earthquake can be attributed to:
a. inflation b. the much higher magnitude of the Northridge earthquake c. the location of the epicenter of the Northridge earthquake in a more vulnerable area d. an increase in population and development in the area during the time between the two earthquakes