Relative to before the price ceiling, how much surplus do producers lose because of the ceiling?
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram which shows the effects of a price ceiling. The initial price and quantity are P0 and Q0, respectively, and the price ceiling is imposed at the price P1. Assume that none of the potential deadweight loss can be avoided.
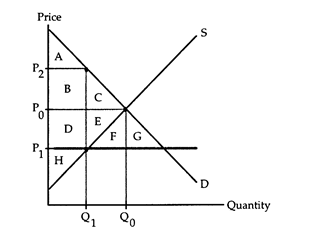
a. Area D + E + H
b. Area D + E
c. Area D + E + F
d. Area H.
b. Area D + E
You might also like to view...
A good or service is considered scarce if
a. any quantity of it can be consumed at a zero price b. the amount people desire exceeds the amount available at a zero price c. the amount people desire exceeds the amount available at any price d. the amount people desire is less than the amount available at any price e. the amount people desire is less than the amount available at a zero price
A written contract between an employer and an employee creates value as long as:
a. the benefits exceed the costs of forming and enforcing it. b. the productivity of the employee is equivalent to the wage. c. on-the-job learning is unimportant. d. the relationship between the employer and the employee is short-term.
Opportunity cost refers to how many inputs a producer requires to produce a good
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the information provided in Scenario 36.6 below to answer the question(s) that follow.SCENARIO 36.6: Following is information pertaining to four surveys:Survey 1: 50 pre-law students at Vanderbilt University are surveyed for a study to see if taking an LSAT preparation course was effective in improving their chance of being admitted to law school.Survey 2: 600 newly hired Houston-area elementary school teachers are surveyed for a study to determine how much salary they were willing to sacrifice to get a job teaching in a school with a high-quality reputation.Survey 3: 950 people are surveyed 6 months after buying a new car for a study to see how satisfied they are with their purchase.Survey 4: 75 people are surveyed in front of 5 different casinos on the Las Vegas Strip fo a
study to determine the average daily gambling budget of a Las Vegas visitor.Refer to Scenario 36.6. Of the four surveys, which is likely to be the least statistically significant? A. Survey 1 B. Survey 2 C. Survey 3 D. Survey 4