Consider distributed optimistic concurrency control in which each server performs local backward
validation sequentially (that is, with only one transaction in the validate and update phase at one
time), in relation to your answer to Exercise 17.4. Describe the possible outcomes when the two
transactions attempt to commit. What difference does it make if the servers use parallel validation?
What will be an ideal response?
At server X, T precedes U. At server Y, U precedes T. These are not serially equivalent because there are Read/
Write conflicts.
T starts validation at server X and passes, but is not yet committed. It requests validation at server Y. If U has
not yet started validation, Y can validate T. Then U validates after T (at both). Similarly for T after U.
T starts validation at server X and passes, but is not yet committed. It requests validation at server Y. If U has
started validation, T will be blocked. When U requests validation at X, it will be blocked too. So there is a
deadlock.
If parallel validation is used, T and U can be validated (in different orders) at the two servers, which is wrong.
You might also like to view...
The __________ method in the Queue interface retrieves and removes the head of this queue, or null if this queue is empty.
a. poll() b. remove() c. peek() d. element()
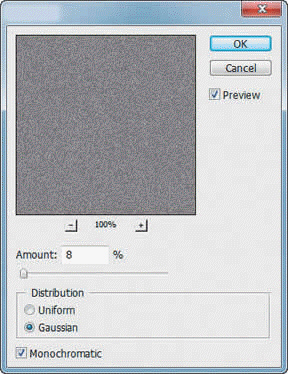 Which of the following can be accomplished by using the dialog box in the accompanying figure?
Which of the following can be accomplished by using the dialog box in the accompanying figure?
A. add sharpness to artwork B. create a consistent texture across an image C. both a. and b. D. neither a. nor b.
Category 6 is an example of a ________ used to connect wired network devices
A) cable B) protocol C) packet D) token
The component that allows you to make a paper-based copy of a body of text is the _____.
a. printer b. scanner c. monitor d. modem