The four scales of atmospheric motion from largest to smallest are:
A) planetary, synoptic, meso, and micro.
B) planetary, soprano, micro, and meso.
C) meso, planetary, micro, bass.
D) micro, meso, synoptic, planetary.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Heat is thermal energy that flows from
A. high energy to low energy. B. hot to cold. C. high thermal pressure to low thermal pressure. D. all of the above
On the windward side of the mountain, is the relative humidity of the parcel increasing or decreasing as it rises from sea level to 2000 meters? Why?
Assume that a parcel of air is forced to rise up and over a 4000-meter-high mountain (as shown). The initial temperature of the parcel at sea level is 30°C, and the lifting condensation level (LCL) of the parcel is 2000 meters. The DAR is 10°C/1000 m and the SAR is 6°C/1000 m. Assume that condensation begins at 100% relative humidity and that no evaporation takes place as the parcel descends.
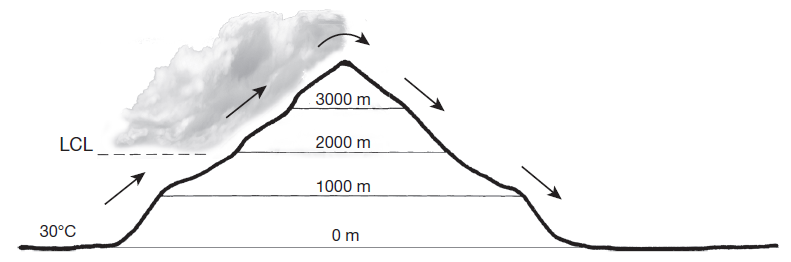
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is not one of the roles of the atmosphere?
A) Energy exchanges between the surface and outer space, creating weather and climate B) Lessening the effects of weathering on the geosphere C) Protection from ultraviolet radiation and the intensity of the Sun D) Providing air for respiratory processes in the biosphere
Which of the following is determined by measuring the amplitude of waves recorded from an earthquake?
A) focus or hypocenter B) intensity C) epicenter D) magnitude