Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as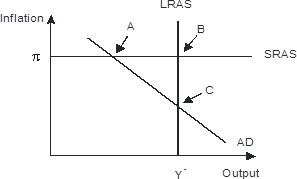
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward
B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward
C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward
D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The ________ of something is the gain or pleasure that it brings
A) rational margin B) marginal cost C) benefit D) opportunity cost E) rational choice
Which of the following is a true statement regarding the economic growth model's predictions and how it actually affects the real world?
A) The growth model predicts that poor countries will catch up with rich countries, but lower-income industrialized countries are not catching up to higher-income industrialized countries as a group. B) The growth model predicts that poor countries should catch up with rich countries, but developing countries are not catching up to lower-income industrialized countries as a group. C) The growth model predicts that poor countries will catch up with rich countries, and this is what we observe across all developmental categories of countries. D) The growth model predicts that poor countries will never catch up with rich countries, but lower-income industrialized countries are catching up to higher-income industrialized countries as a group.
The Cournot equilibrium can be found by treating ________ as a pair of simultaneous equations and by finding the combination of Q1 and Q2 that satisfy both equations
A) the reaction curves for firms 1 and 2 B) the market supply curve and the market demand curve C) the contract curve and the market demand curve D) the contract curve and the market supply curve E) the firm's supply curve and the firm's demand curve
If the Federal Reserve was to buy U.S. dollars on the foreign exchange market, a likely result will be: a. a rightward shift in the dollar supply curve
b. at least a temporary decline in the exchange value of the U.S. dollar. c. at least a temporary increase in the exchange value of the U.S. dollar. d. both (a) and (b)